Cannabis
The Science Behind Cannabis Trichromes
Cannabis trichromes are tiny, hair-like structures found on the surface of cannabis flowers, leaves, and even stems. These structures are responsible for producing the cannabinoids and terpenes that give cannabis its unique properties. While many people are familiar with the effects of cannabis, few understand the science behind these tiny structures that play a critical role in its production. In this article, we will delve into the science behind cannabis trichromes and explore the benefits they offer.
Introduction to Cannabis Trichromes
Trichomes are small, hair-like structures that grow on the surface of many plants, including cannabis. These structures are responsible for producing the resin that contains the cannabinoids and terpenes that give cannabis its unique properties, including its psychoactive effects, flavor, and aroma.
The term “trichome” comes from the Greek words “trikhos” (meaning hair) and “oma” (meaning tumor). While trichomes may look like tiny tumors. They are actually highly specialized structures that have evolved to protect plants from predators, UV radiation, and other environmental stressors.
What are Trichomes?
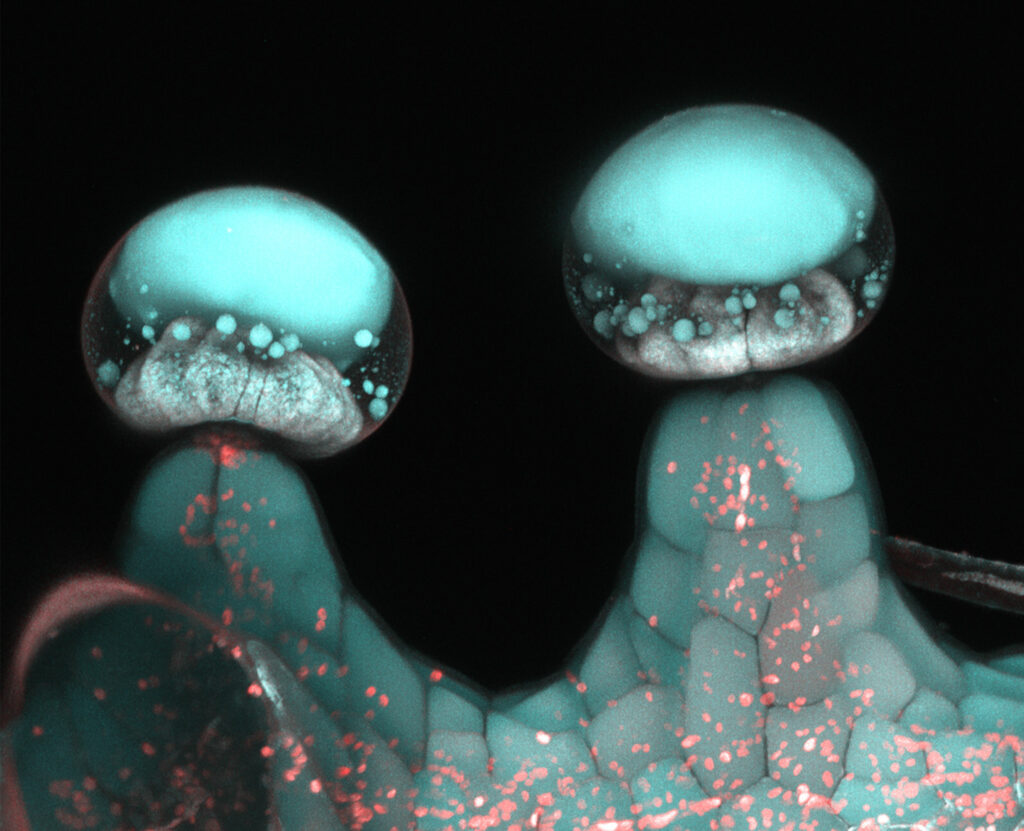
Trichomes are tiny, glandular structures that grow on the surface of the cannabis plant. These structures are made up of three main components: the stalk, the head, and the bulbous gland. The stalk connects the trichome to the surface of the plant, while the head contains the resin-producing gland. The bulbous gland is located at the base of the head and helps to anchor the trichome in place.
Cannabis trichomes come in many different shapes and sizes, ranging from tiny, mushroom-shaped structures to large, stalk-like appendages. The size and shape of trichomes can vary depending on the strain, growing conditions, and other factors.
Types of Trichromes in Cannabis
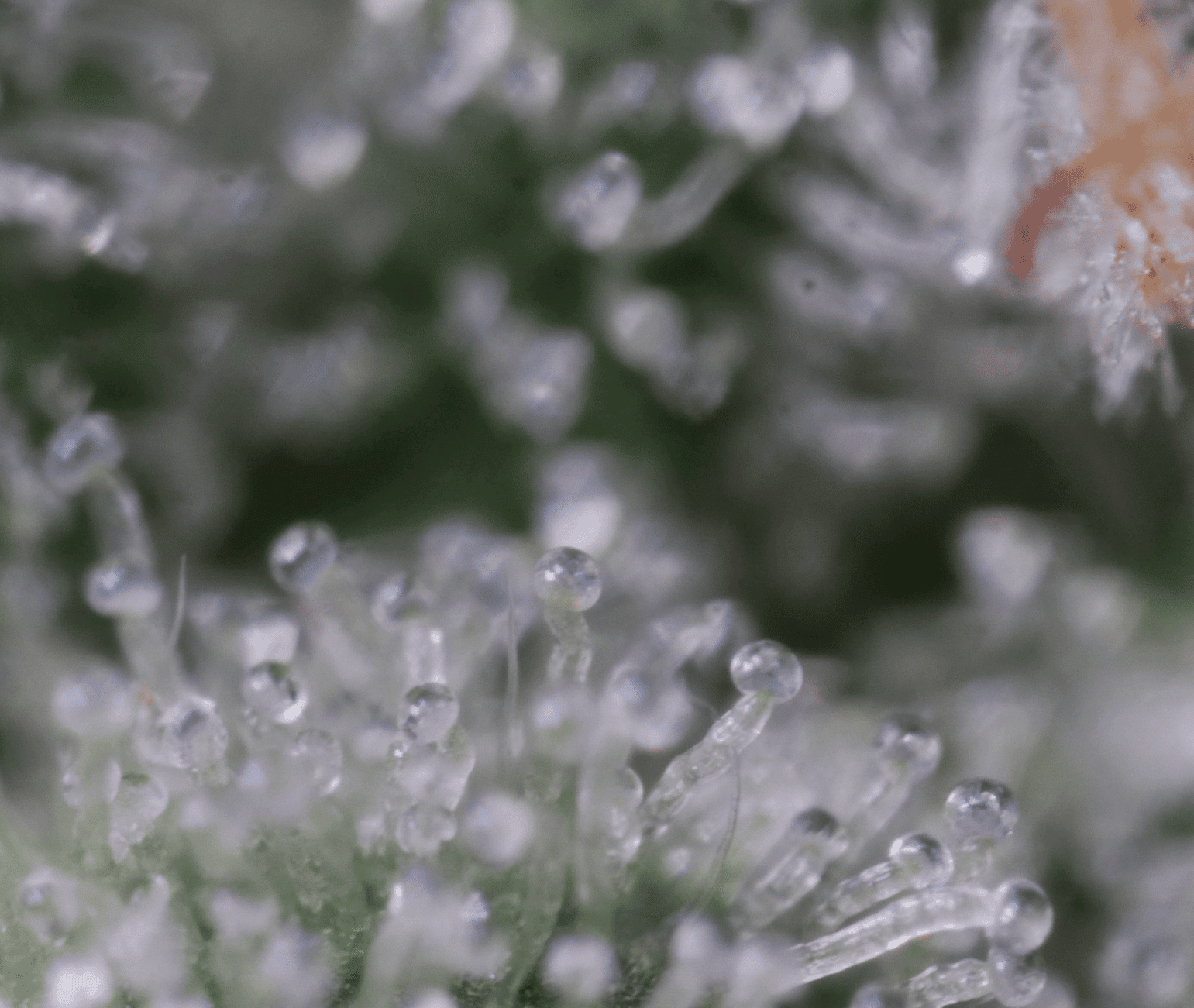
There are three main types of trichomes that grow on cannabis plants: capitate stalked trichomes, capitate sessile trichomes, and bulbous trichomes.
Capitate stalked trichomes are the largest and most abundant type of trichome found on cannabis plants. These trichomes have a stalk that is on the surface of the plant. They have a large, resin-producing gland at the head.
Capitate sessile trichomes are smaller and less abundant than capitate stalked trichomes. These trichomes have a gland that is directly part of the surface of the plant, without a stalk.
Bulbous trichomes are the smallest and least abundant type of trichome found on cannabis plants. These trichomes are round and contain a single gland that produces resin.

The Anatomy of Trichromes
Trichomes are complex structures that contain a variety of specialized cells, each with a specific function. The head of the trichome contains the resin-producing gland, which is made up of two types of cells: secretory cells and basal cells.
Secretory cells are responsible for producing and storing the resin that contains the cannabinoids and terpenes found in cannabis. These cells are highly specialized and contain large amounts of lipid and terpenoid compounds.
Basal cells are the support cells that surround the secretory cells. These cells provide structural support and help to regulate the production and release of resin.
The stalk of the trichome contains a variety of other specialized cells, including epidermal cells, vascular cells, and trichome stem cells. These cells play a crucial role in the development and function of the trichome.
The Function of Trichromes in Cannabis
Trichomes play a critical role in the production of the resin that contains the cannabinoids and terpenes found in cannabis. These compounds are responsible for the psychoactive effects, flavor, and aroma of the plant.
Trichomes also play a vital role in protecting the plant from predators, UV radiation, and other environmental stressors. The resin produced by trichomes contains compounds that are toxic to many insects and animals, making it an effective defense mechanism.
The Science Behind Trichromes Production
The production of trichomes in cannabis is a complex process that is influenced by a variety of factors. Including genetics, growing conditions, and environmental stressors.
Cannabis plants produce trichomes in response to stress, such as exposure to UV radiation, high temperatures, or pests. The production of trichomes is also influenced by the plant’s genetics, with some strains producing more trichomes than others.
Factors Influencing Trichrome Production
The production of trichomes in cannabis is influenced by a variety of factors, including light, temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels.
Light is one of the most important factors influencing trichome production in cannabis. Plants need a specific type and intensity of light to produce trichomes effectively. High-intensity light, such as that produced by LED grow lights, can stimulate trichome production in cannabis plants.
Temperature and humidity also play a crucial role in trichome production. Cannabis plants thrive in a specific range of temperatures and humidity levels, and deviations from these optimal conditions can significantly impact trichome production.
Nutrient levels, particularly those of nitrogen and phosphorus, can also influence trichome production in cannabis plants. Plants that are deficient in these nutrients may produce fewer trichomes than those that have enough to feed on.

Understanding the Role of Terpenes in Trichrome Production
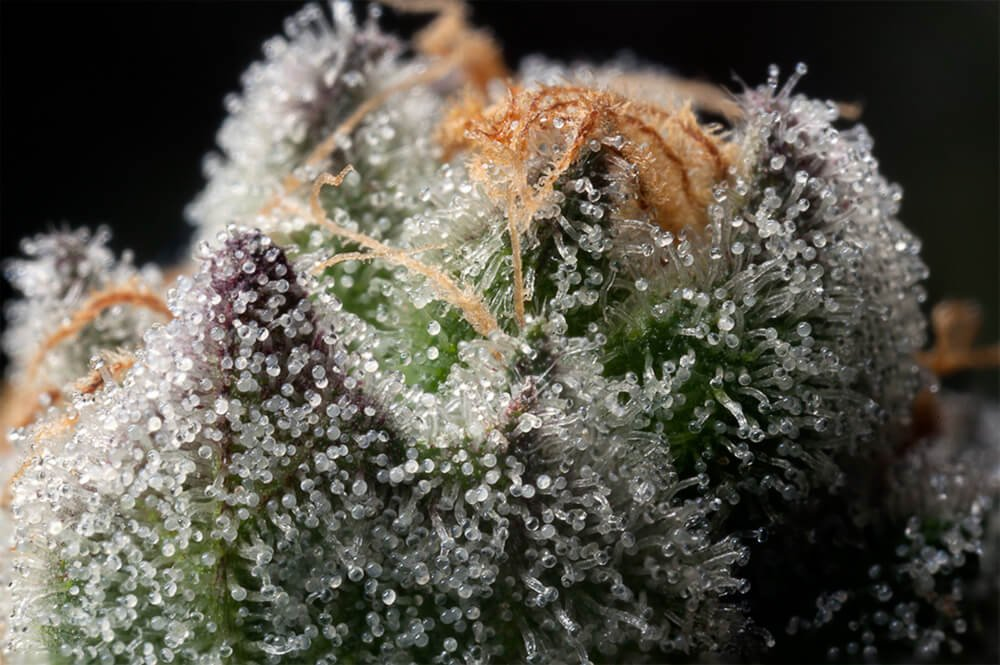
Terpenes are aromatic compounds are in many plants, including cannabis. These compounds are responsible for the distinctive flavors and aromas of cannabis strains and play a crucial role in trichome production.
Research has shown that terpenes can influence the production of trichomes in cannabis plants. Some terpenes, such as myrcene and linalool, stimulate trichome production. While others, such as limonene and pinene, may inhibit trichome production.
The Benefits of Trichromes in Cannabis
Trichomes are essential for the production of high-quality cannabis. As well as, these structures contain the cannabinoids and terpenes that give cannabis its unique properties. Including its psychoactive effects, flavor, and aroma.
Trichomes also play a crucial role in protecting the plant from predators and environmental stressors. The resin produced by trichomes contains compounds that are toxic to many insects and animals, making it an effective defense mechanism.
Conclusion: The Future of Trichrome Research
The study of trichomes and their role in cannabis production is an exciting area of research. As our understanding of these structures grows. we may, be able to develop new techniques and technologies to optimize trichome production and improve the quality and potency of cannabis.
In conclusion, trichomes are a critical component of cannabis production. These tiny, crystal-like structures play a vital role in the potency, flavor, and aroma of cannabis strains, as well as in the plant’s defense against predators and environmental stressors. By understanding the science behind trichome production and function, we can continue to develop new and innovative ways to cultivate high-quality cannabis.